Specular and Diffusion ReflectionHow Light Reflects MooMooMath and Science
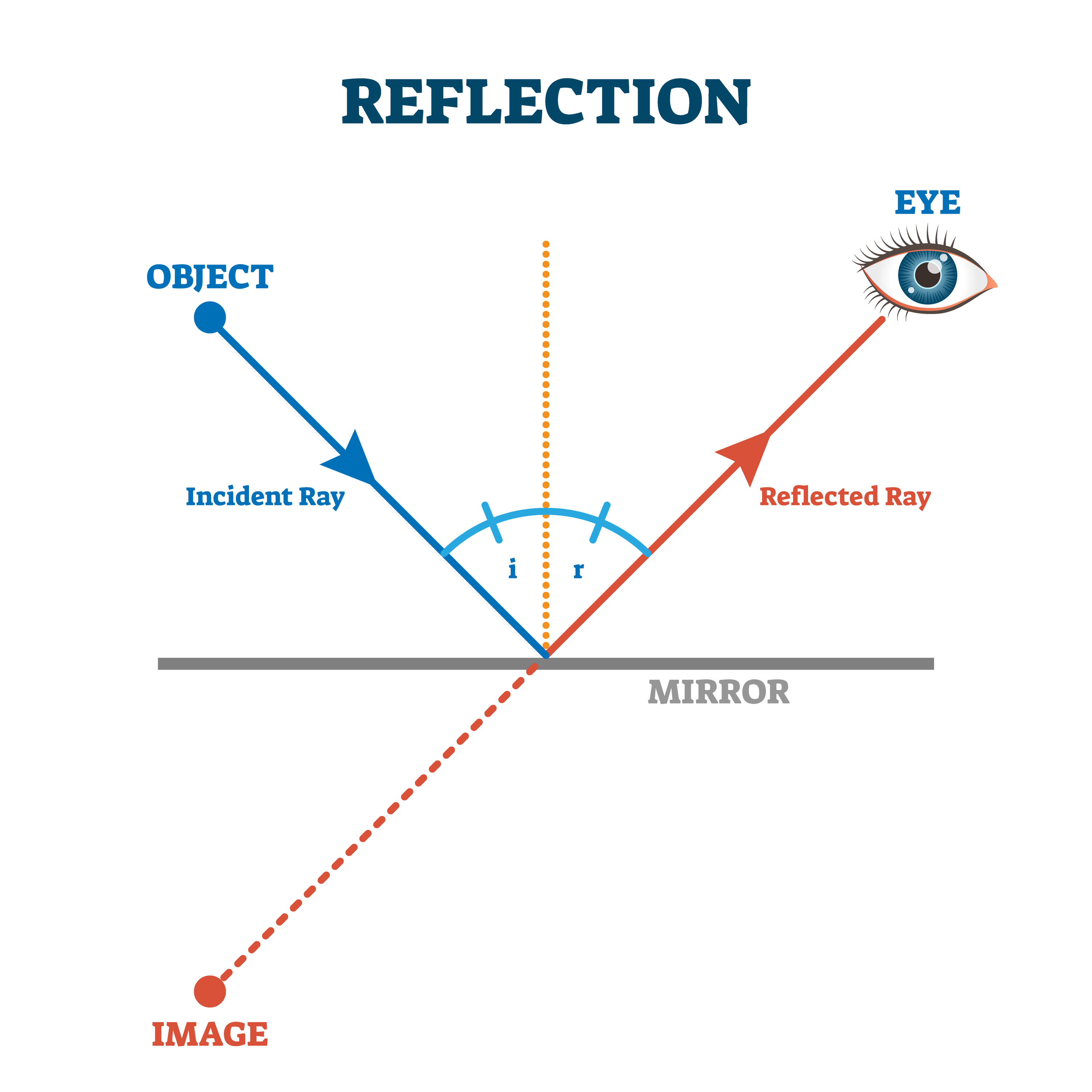
The angle of reflection is measured between a ray of light which has been reflected off a surface and an imaginary line called the normal. The normal. , the normal is an imaginary line drawn on a ray diagram perpendicular to, so at a right angle to (90 ), to the boundary between two media. If the boundary between the media is curved then the.
Light Refraction Diagram Water Reflection, PNG, 3073x1897px, Light, Angle Of Incidence, Area
Explain reflection from mirrors, describe image formation as a consequence of reflection from mirrors, apply ray diagrams to predict and interpret image and object locations, and describe applications of mirrors Perform calculations based on the law of reflection and the equations for curved mirrors Section Key Terms Characteristics of Mirrors

Reflection of Light Definition, Types, Laws & More Leverage Edu
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated.. Diagram of specular reflection. In the diagram, a light ray PO strikes a vertical mirror at point O,.

25.2 The Law of Reflection College Physics OpenStax
The Mirror Equation - Convex Mirrors. The ray nature of light is used to explain how light reflects off of planar and curved surfaces to produce both real and virtual images; the nature of the images produced by plane mirrors, concave mirrors, and convex mirrors is thoroughly illustrated.

Specular And Diffuse Reflection Vector Illustration Diagram Stock Illustration Download Image
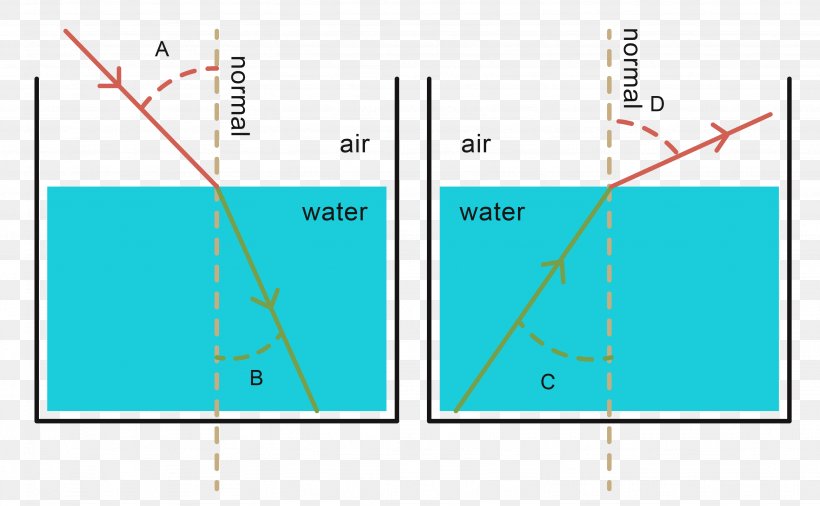
Reflection is a phenomenon in which a wave traveling through a medium reflects at the interface of another medium. In optics, reflection takes place when light is incident at the interface of the two media. The ray of light returns to the first medium without any change in velocity. Reflection Example.

Definition Specular Reflection Photokonnexion
The diagrams show a water wave being reflected at a barrier,. Each individual reflection still obeys the law of reflection, but the different parts of the rough surface are at different angles.
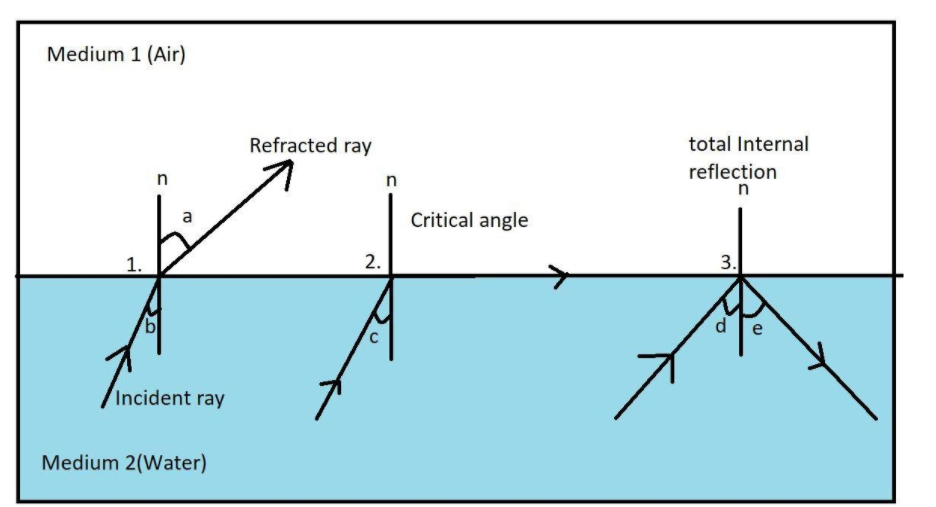
Explain total internal reflection with diagram.
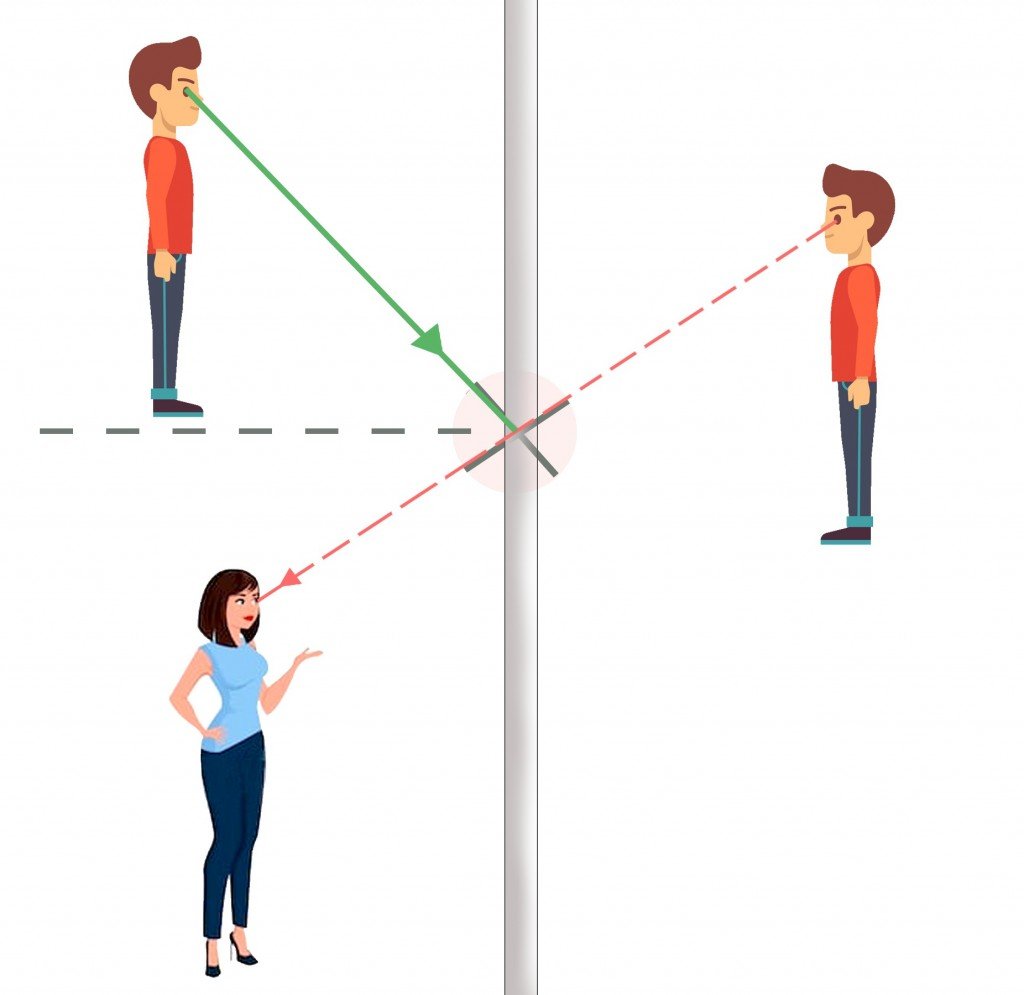
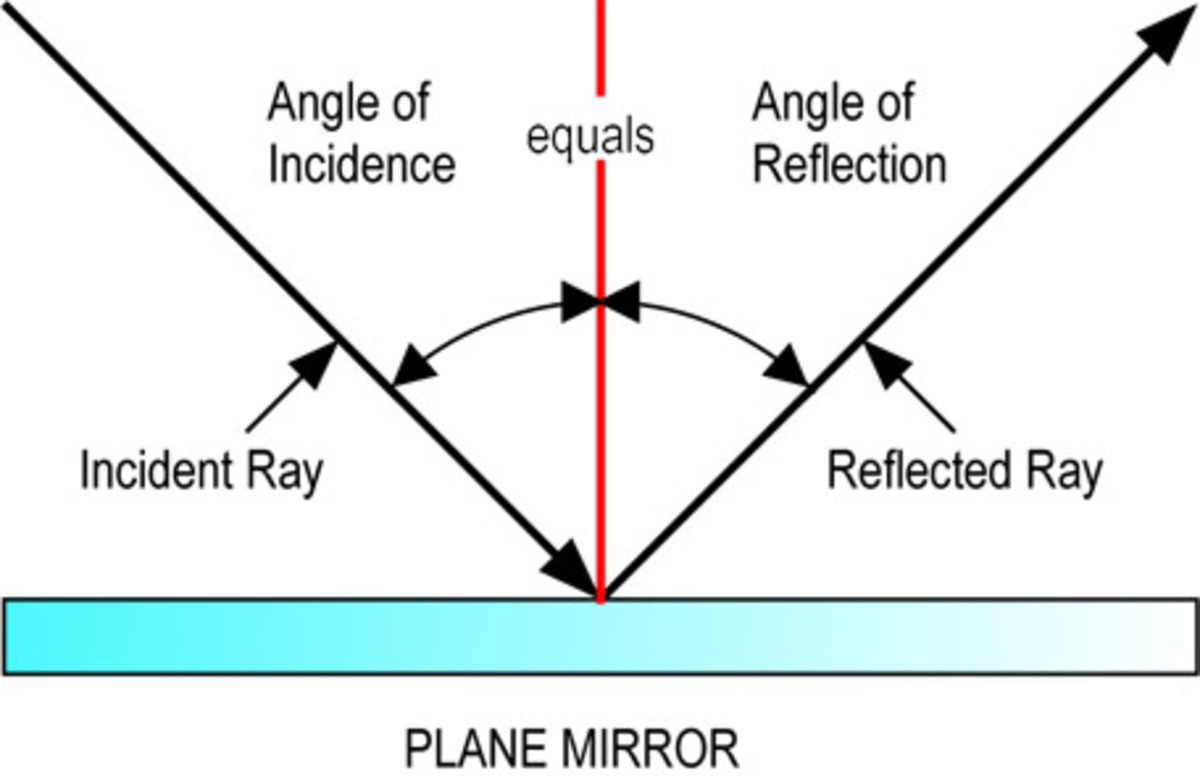
The law of reflection (in physics) states that when a light ray is incident on a plane surface, the incident ray, the reflected ray and the "normal" to the surface of the mirror all lie in the same plane. It also states that the angle the incident ray makes with the normal is equal to the angle that the reflected ray makes with the normal.
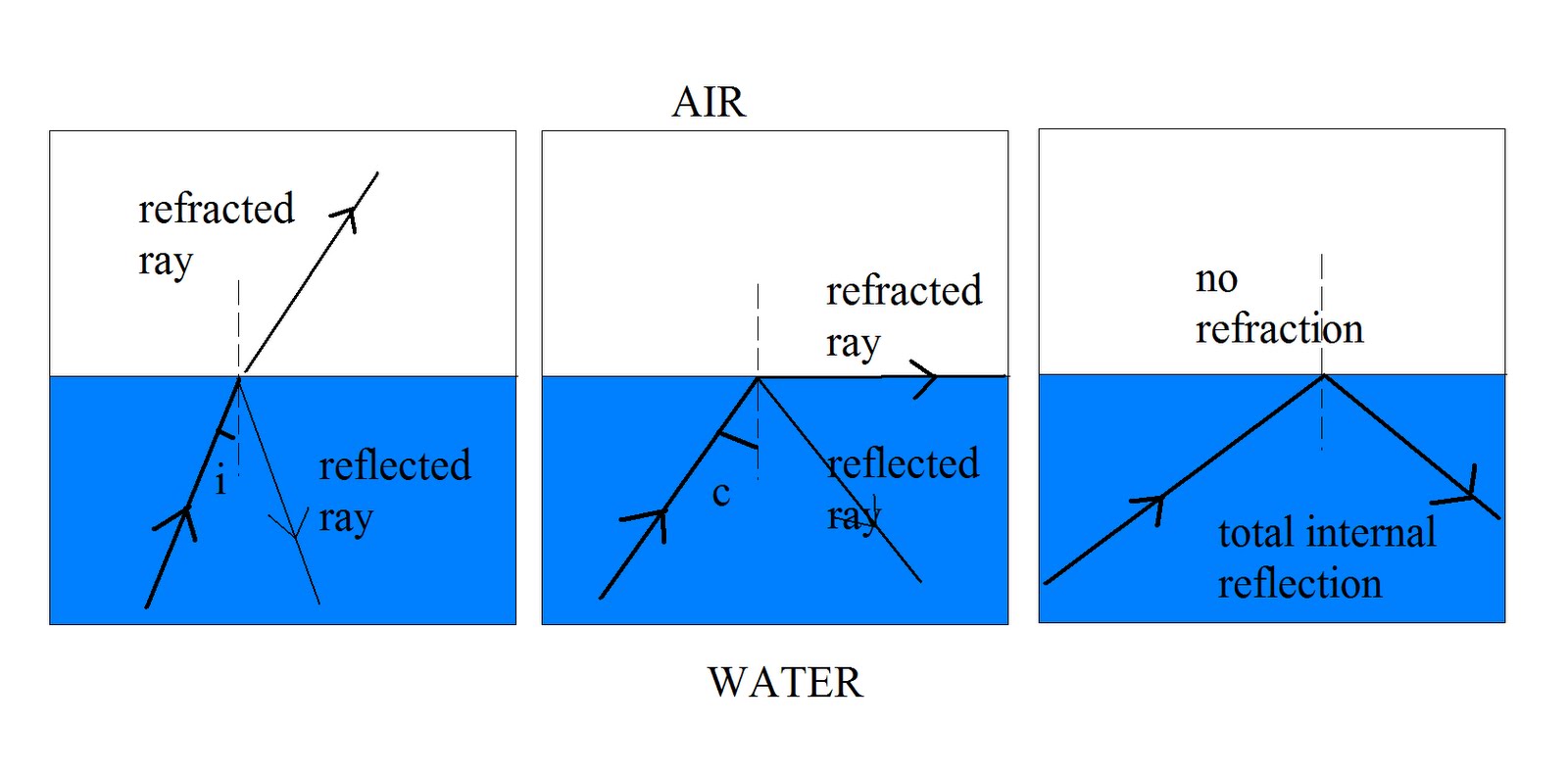
Get Into Physics A Bit of Internal Reflection
The reflection of light 7-25-00 Sections 23.1 - 23.3 Rays and wave fronts.. Consider an object placed a certain distance in front of a mirror, as shown in the diagram. To figure out where the image of this object is located, a ray diagram can be used. In a ray diagram, rays of light are drawn from the object to the mirror, along with the.

Khayyam Reflective water with GLSL, Part II
The law of reflection defines that upon reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is equal to the angle of the incident ray, with respect to the normal to the surface that is to a line perpendicular to the surface at the point of contact.
What Is The Law Of Reflection Definition And A Simple Explanation
Light - Reflection, Refraction, Physics: Light rays change direction when they reflect off a surface, move from one transparent medium into another, or travel through a medium whose composition is continuously changing. The law of reflection states that, on reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is equal to the angle of the incident ray.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ReflectionLaw-5946c6dd5f9b58d58a2f2efc.png)
How Reflection Works in Physics
It is given by. n1 sinθ1 = n2 sinθ2. n 1 sin θ 1 = n 2 sin θ 2. 16.6. When the incident angle equals the critical angle ( θ1 θ 1 = θc θ c ), the angle of refraction is 90° ( θ2 θ 2 = 90°). Noting that sin 90° = 1, Snell's law in this case becomes. n1 sinθ1 = n2. n 1 sin θ 1 = n 2.

Reflection of Light Definition, Types, Laws & More Leverage Edu
To draw a ray diagram showing reflection: Draw two rays from the object to the mirror. Each ray should obey the law of reflection. Trace the rays back using dashed lines, until they meet.
Reflection and Refraction of Light & It's Applications hubpages
The reflection and refraction of light 7-27-99 Rays and wave fronts. Light is a very complex phenomenon, but in many situations its behavior can be understood with a simple model based on rays and wave fronts. A ray is a thin beam of light that travels in a straight line.. The diagram shows the principal axis, focal point (F), and center of.

Reflection of Light Definition, Types, Laws & More Leverage Edu
The diagram below shows the reflected wavefronts and the reflected ray. Regardless of the angle at which the wavefronts approach the barrier, one general law of reflection holds true: the waves will always reflect in such a way that the angle at which they approach the barrier equals the angle at which they reflect off the barrier.

Laws Of Reflection Diagram Reflection, Science revision, Light reflection
This question presents us with a diagram showing a ray of light incident on a flat, reflective surface and asks us to calculate the angle of reflection. We are given an angle of 1 3 0 ∘ on the diagram, but we should notice that this is not, in fact, the angle of incidence.

Angle of incidence physics Britannica
We use the diagram shown below to answer the questions. c) q = 90 - r = 90 - 34 = 56 ° A ray of light is reflected by two parallel mirrors (1) and (2) at points A and B. The ray makes an angle of 25° with the axis of the two mirrors. b) What is the angle of reflection at the point of incidence B?